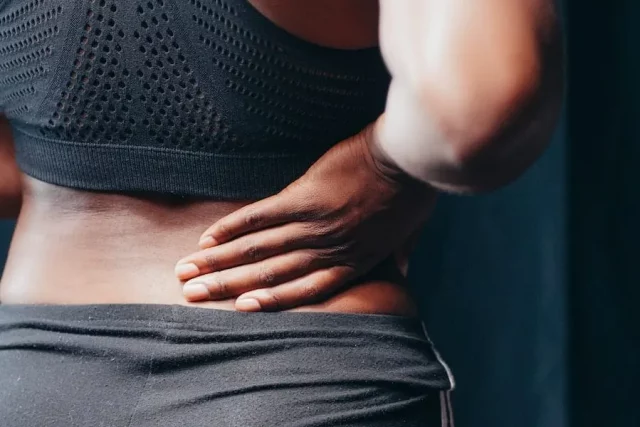
Bursitis is a painful bursal swell. The bursae cushion your ligaments, tendons, and muscles, which are sacs filled with fluid. Bursae aid in the smooth movement of ligaments, tendons, and muscles over bone when they function appropriately. However, the region around the bursae becomes highly tender and unpleasant when they swell. Hip bursae that are affected by trochanteric bursitis enlarge.
Bursitis is not just a hip problem. Additionally, the elbow, knee, and shoulder joints are susceptible.
Definition And Types Of Hip Bursitis
Hip bursitis, sometimes referred to as higher trochanter pain syndrome, is inflammation of the bursa, a cushion in the hip that prevents muscles and tendons from rubbing against the bone. Bursitis can affect other areas of your body, such as the shoulders, knees, or elbows, due to the 160 bursae (the plural version of bursa) that make up an adult’s body.
The bursa on the inside or outside of your hip might become inflamed in hip bursitis. Depending on where the damaged bursa is and if it is inflamed, the kind of hip bursitis you can get will vary. The three main categories of hip bursitis are:
Trochanteric bursitis
The bony protrusion at the top of your thighbone on the outside of your hip is called the trochanter. The outside of your hip and your outside thigh may hurt.
Septic hip bursitis
Septic hip bursitis results from an infected bursa. Hip bursitis that is septic can be dangerous and present with additional symptoms like fever, fatigue, and sickness.
Ischial bursitis
An irritated bursa on the groin side of the hip can occasionally cause pain in the upper buttock or groin.
Hip Bursitis Treatment
Hip bursitis unquestionably needs a prompt response and effective therapy, which is a crucial point that you must not overlook. The nearly exclusively nonoperative treatments for hip bursitis include non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs), stretching, physical therapy, and, in certain cases, corticosteroid injections. When nonoperative treatment fails to improve resistant patients, the trochanteric bursa is surgically removed. This session examines the diagnosis and treatment of trochanteric bursitis and emphasizes the need for interprofessional teamwork in delivering well-coordinated care and improving patient outcomes. The next few paragraphs will go into greater detail about some of the treatments.
Nonsurgical Treatments
Primary care physicians, physiatrists (specialists in physical medicine and rehabilitation), sports medicine physicians, and orthopedic surgeons are among the medical professionals who can treat hip bursitis. Some suggested therapies include:
Modification of rest and activity
Rest and other methods to reduce inflammation are typically effective when hip bursitis results from an injury or overuse. Sports and/or prolonged standing are activities that those with hip bursitis should avoid because they will exacerbate and inflame the bursa. A doctor may also suggest using crutches, a cane, or shoe inserts to relieve strain on the hip.
NSAIDs
Ibuprofen, aspirin, naproxen, and cox-2 inhibitors (Celebrex) are examples of anti-inflammatory drugs that can alleviate hip bursitis-related swelling, irritation, and pain. Regular NSAID use may have gastrointestinal, cardiac, and kidney issues as side effects. Due to this, doctors ordinarily do not advise using NSAIDs regularly for a long time.
Anti-inflammatory topical medicines
Many over-the-counter topical pain medications have salicylates, with a slight anti-inflammatory action. Numerous products containing Aspercreme and Sportscreme are examples of topical salicylates. NSAIDs taken orally typically have more negative effects than topical medicines. Other topical products need a prescription from a doctor.
Corticosteroid injection
Corticosteroid injections may be advised if symptoms cannot be effectively managed by rest, NSAIDs, or even just physical therapy. The doctor may employ ultrasonography to precisely place the injection into the bursa because the afflicted bursa is located deep beneath the skin.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy may be recommended by a doctor to aid with existing bursitis and stop further flare-ups. The quadriceps and gluteals may be strengthened, and the iliotibial band may be stretched, as part of physical therapy’s objectives (IT band). Athletes can learn the right form for running and jumping.
Needle tenotomy
To encourage the development of new, better tendon tissue, needle tenotomy involves making very small holes in the tendon. A local anesthetic is used during this treatment, and needles are used to puncture the tendon and skin. Tenotomy can be paired with prolotherapy, a corticosteroid injection, a PRP injection, or lavage (a technique that “washes away” calcified deposits in the tendon).
Tenex is an ultrasonic-powered type of needle tenotomy. A doctor should be trained to utilize a particular, patented machine for it. Through a little skin incision, the Tenex probe is implanted. Patients receive local anesthesia, just like with conventional tenotomies.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be necessary in particularly difficult cases of persistent hip bursitis, such as:
Iliotibial (IT) band release and tendon repair
The trochanteric bursa may become irritated and inflamed as a result of the IT band being overly tight or a tendon injury. Surgical options include tendon repair or lengthening of the IT band (IT band release). The unwanted friction might be lessened by these soft tissue adjustments and repairs.
Larger trochanter osteotomy
Osteotomy is the medical term for cutting a bone. A surgeon will remove a little piece of the greater trochanter bone during this osteotomy surgery (which is part of the femur, or thigh bone). The stress and friction that led to the hip pain can be lessened by this adjustment.
Bursectomy
A hip incision is created during a typical bursectomy, and the afflicted bursa is then removed. To reduce the chance of problems and speed healing, some doctors conduct arthroscopic bursectomies using a tiny incision.
These treatments could all be carried out in the same surgery. The recommended surgical procedure type is determined by the patient’s symptoms as well as other aspects of their lifestyle and general health.
We sincerely hope that you and your loved ones will not come into contact with this sickness, but even if it does, medical advancements have provided us with many effective treatments. Therefore, try not to worry in advance and take good care of yourself for as long as you can.