Mold is a serious health concern in most homes that many aren’t aware of. When mold issues are raised, most people inspect their shower curtains, the basement, and under the sink. However, mold can grow anywhere, including on the roof, drywall, and Christmas trees. There are currently over 1000 mold types found in American homes.
However, not all mold types are dangerous. Allergenic molds are the least dangerous as they cause allergies. On the other hand, pathogenic and toxigenic mold types are the most hazardous.
What Is Mold?
Mold is typically a fungus that grows in warm and moist environments. It is commonly found in the kitchen, basements, bathrooms, and other highly humid areas. Mold problems often occur in homes due to water leaks, poor ventilation, and floods. Mold spreads through airborne spores, which humans can also inhale.
Mold sickness occurs once you inhale airborne spores in your body. Mold spores in the body release toxic substances known as mycotoxins, which produce immune reactions for some and are extremely toxic to others. Most people with mold sickness have high amounts of mold toxicity (total body burden) in their bodies.
Who Are Susceptible To Mold Infection?
Like other diseases, some people develop symptoms of infection faster, while others don’t experience symptoms at all. The following categories can develop symptoms even with mild exposure:
- People with chronic diseases – individuals diagnosed with chronic respiratory conditions, such as asthma and obstructive pulmonary disorder, can develop mold poisoning after a small exposure. Mold spores can worsen these conditions.
- People allergic to mold – surprisingly, some people are super allergic to mold, which worsens their reaction to exposure. If you are allergic to mold, you should minimize contact with infected air, as long exposures can cause severe problems.
- People with compromised immunity – immunocompromised people have low immune resistance, making them vulnerable to mold exposure. Bad nutrition, smoking, and alcohol also suppress your immunity, increasing susceptibility to mold sickness.
Symptoms Of Mold Infection
Exposed persons react to mold toxicity differently. However, several factors determine how long it takes for mold to cause an infection. These factors include:
- Allergies and sensitivities – your reaction to mold differ from other people’s. Your degree of sensitivity to mold significantly influences how quickly you develop the symptoms. If you are not allergic to mold, one-time exposure won’t make you sick.
- Amount and duration of mold exposure – the amount and duration of mold exposure also determines how long it will take before mold sickness symptoms start. Generally, long exposure and large amounts will most likely lead to an infection. If the exposure lasts a few minutes, you won’t likely develop these symptoms.
That said, below are the signs of mold sickness:
- Cognitive difficulties, such as poor memory, brain fog, and anxiety
- Numbness and tingling of extremities
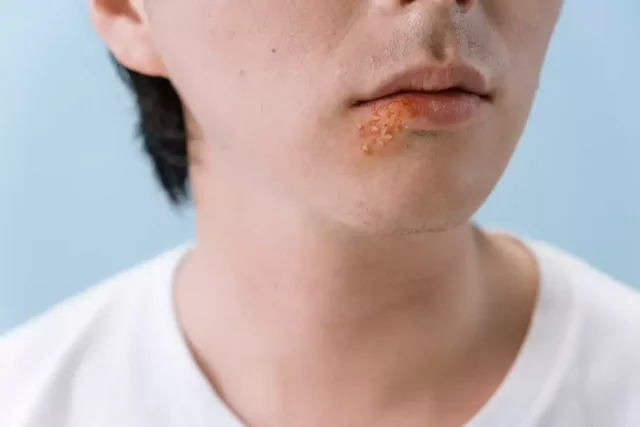
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Unexplained or sudden weight gain or weight loss
- Pain in the abdomen and muscles
- Dizziness and vertigo
- Fatigue that affects daily activities
- Excessive dehydration
- Tinnitus or ringing in the ears
- Digestive problems, such as persistent bloating and low tolerance to food
- Unexplained mood changes
- Wheezing and shortness of breath
- Runny nose and watery eyes
- Coughing and persistent sinusitis
In severe cases, mold spores can grow in various body parts, specifically the sinuses and lungs. This causes serious respiratory infections.
Conclusion
Even though mold exposure and sickness symptoms are uncommon, most health care providers struggle before pinpointing the underlying cause of your presenting symptoms. Most people suffering from mold sickness are misdiagnosed with conditions like fibromyalgia, anxiety, depression, and Lyme disease. That said, if you have witnessed signs of mold growth in your home, be sure to contact mold remediation experts and seek medical interventions.