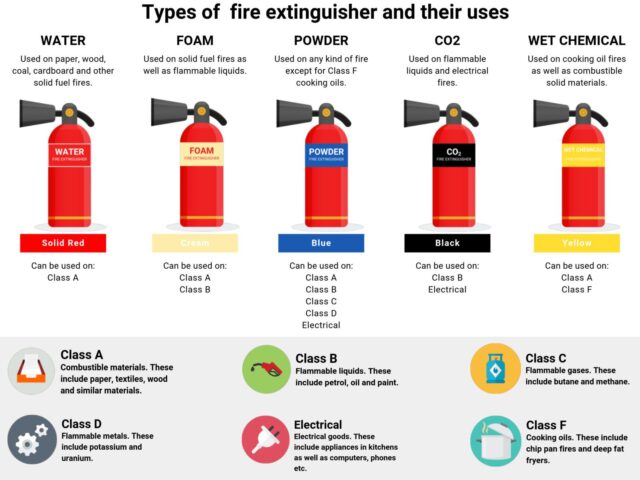
Fire extinguishers are a crucial component of fire safety in homes, workplaces, and public areas. They are designed to control and extinguish small fires, providing the necessary time to evacuate safely. Each fire extinguisher is equipped with a label containing a letter and a number, which serves specific purposes in identifying the type of fire it can combat and the size of that extinguisher.
What does the number indicate?
The number on a fire extinguisher label indicates the size and effectiveness of the unit. Higher numbers generally suggest a larger capacity, meaning the extinguisher can discharge more extinguishing agents and is effective for larger fires. For example, a 10-A extinguisher is designed for more significant fire exposure than a 2-A extinguisher. The label helps users quickly assess which extinguisher to use for various fire classes.
Understanding Fire Extinguisher Classifications
Fire extinguishers are categorized based on the type of fire they are designed to combat. The letters on the labels represent these classes:
- Class A: Fires involving ordinary combustibles like wood, paper, and cloth.
- Class B: Fires involving flammable liquids such as gasoline and oil.
- Class C: Fires involving electrical equipment.
- Class D: Fires involving combustible metals.
- Class K: Fires involving cooking oils and fats.
Each class has specific requirements, and the inclusion of numbers further clarifies the effectiveness of each model.
The Significance of the Number on the Label
The number associated with each letter classifies extinguishers by their effectiveness and size. For instance, a Class A extinguisher may have a rating of 2-A, 10-A, etc. The number signifies the amount of extinguishing agent available, which affects how long and how effectively the extinguisher can operate.
| Class | Rating | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | 2-A | Can extinguish fires involving 2.5 gallons of water |
| A | 10-A | Can extinguish fires involving 10 gallons of water |
| B | 5-B | Can extinguish fires involving 5 square feet of flammable liquid |
| C | 10-C | Suitable for electrical fires up to 10,000 volts |
Example of Ratings:
- A 4-A extinguisher can handle fires comparable to 4.0 gallons of water.
- A 20-B extinguisher is effective for fires covering an area of 20 square feet.
How to Choose the Right Fire Extinguisher
Selecting the appropriate fire extinguisher is critical for safety. Users should consider the potential fire hazards in their environment. For example, kitchens may require a Class K extinguisher for cooking oils, whereas offices might need Class C extinguishers for electrical equipment.
- Assess the Environment: Identify possible fire risks.
- Understand Fire Classes: Match extinguishers with fire types.
- Examine Extinguisher Size: Choose sizes based on expected fire potential.
| Area | Recommended Fire Extinguisher | Class Type |
|---|---|---|
| Kitchen | 1-A:10-B:C | A, B, C |
| Garage | 4-A:20-B | A, B |
| Warehouse | 10-A:40-B | A, B |
| Laboratory | 10-B:C | B, C |
Maintenance and Inspection of Fire Extinguishers
To ensure fire extinguishers are operational when required, regular maintenance and inspections are necessary. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) recommends that fire extinguishers undergo an annual inspection and a detailed examination every six years.
Key maintenance tasks include:
- Visual Checks: Monthly checks for physical damage, pressure gauge readings, and tampering.
- Professional Inspections: Every year, a professional should test the unit and refill it as needed.
- Hydrostatic Testing: This should occur every 5-12 years depending on the extinguisher type, ensuring structural integrity.
Fire Extinguisher Training
In addition to having the right equipment, training in its use is vital. Emergency responders suggest that staff and family members receive training in the use of fire extinguishers. Training increases response speed in emergencies and improves safety during fire incidents.
Training should cover:
- Recognizing different fire classes.
- Understanding the proper use of extinguishers.
- Conducting regular fire drills to practice evacuation and use of extinguishers.
The Importance of Compliance
Fire safety regulations often require specific extinguishers in various settings. Failure to comply can lead to severe penalties and increased risk of fire hazards. Businesses and property owners should stay informed about local fire codes and maintain the equipment to meet these standards.
Conclusion
Understanding the labeling system of fire extinguishers, including what the number indicates, is crucial for effective fire safety management. The letters and numbers help users quickly identify the right extinguisher for various fire hazards. Regular maintenance, training, and compliance with fire safety regulations significantly enhance the effectiveness of fire extinguishers, ultimately saving lives and property. Proper knowledge and preparation can make all the difference in an emergency. Always prioritize safety by reviewing and understanding your fire extinguishing options.